Computes the (signed) Area Under the Curve (AUC) of a path, defined by vectors of x and y coordinates, as compared to an ideal line passing through the start and end points.
Arguments
- x_vector
x-coordinates of the executed path.
- y_vector
y-coordinates of the executed path.
- x_start
x-coordinate of the start point of the ideal line. Defaults to the first value in
x_vector.- y_start
y-coordinate of the start point of the ideal line. Defaults to the first value in
y_vector.- x_end
x-coordinate of the end point of the ideal line. Defaults to the last value in
x_vector.- y_end
y-coordinate of the end point of the ideal line. Defaults to the last value in
y_vector.- geometric
Whether the sign of areas that stem from a movement in the reverse direction of the ideal line should be reversed. Defaults to
FALSE, indicating an time-based instead of geometric interpretation. Only impacts the AUC if the trajectory is not monotonically increasing relative to the ideal line.
Details
The ideal line is a line, not a line segment, i.e., it has infinite length. The supplied vectors are assumed to be ordered by time. Counterclockwise deviations from the ideal line are considered positive, clockwise deviations as negative for the computation of the AUC. Thus, negative AUCs are possible.
References
Pfister, R., Tonn, S., Schaaf, M., Wirth, R. (2024). mousetRajectory: Mouse tracking analyses for behavioral scientists. The Quantitative Methods for Psychology, 20(3), 217-229. doi:10.20982/tqmp.20.3.p217
Examples
x_vals <- c(0, 0, 0, 1, 2)
y_vals <- c(0, 1, 2, 2, 2)
plot(x_vals, y_vals, type = "l")
lines(c(0, 2), c(0, 2), lty = "dashed", lwd = 2) # ideal
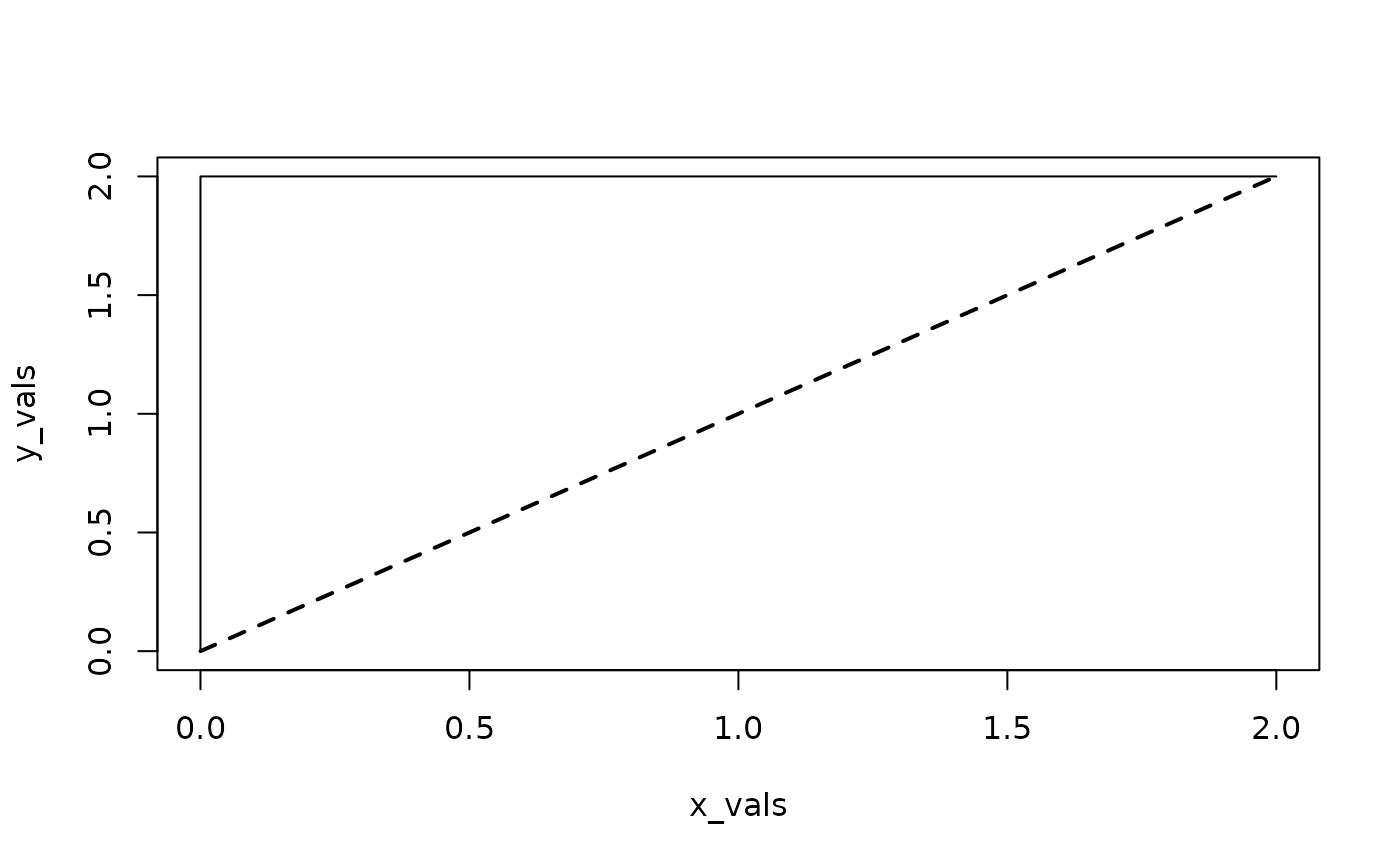 auc(x_vals, y_vals) # counterclockwise deviation: positive
#> [1] 2
x_vals <- c(0, 1, 2, 2, 2)
y_vals <- c(0, 0, 0, 1, 2)
auc(x_vals, y_vals) # clockwise deviation: negative
#> [1] -2
plot(x_vals, y_vals, type = "l")
lines(c(0, 2), c(0, 2), lty = "dashed", lwd = 2) # ideal
auc(x_vals, y_vals) # counterclockwise deviation: positive
#> [1] 2
x_vals <- c(0, 1, 2, 2, 2)
y_vals <- c(0, 0, 0, 1, 2)
auc(x_vals, y_vals) # clockwise deviation: negative
#> [1] -2
plot(x_vals, y_vals, type = "l")
lines(c(0, 2), c(0, 2), lty = "dashed", lwd = 2) # ideal
 x_vals <- -x_vals
auc(x_vals, y_vals) # now it is counterclockwise again
#> [1] 2
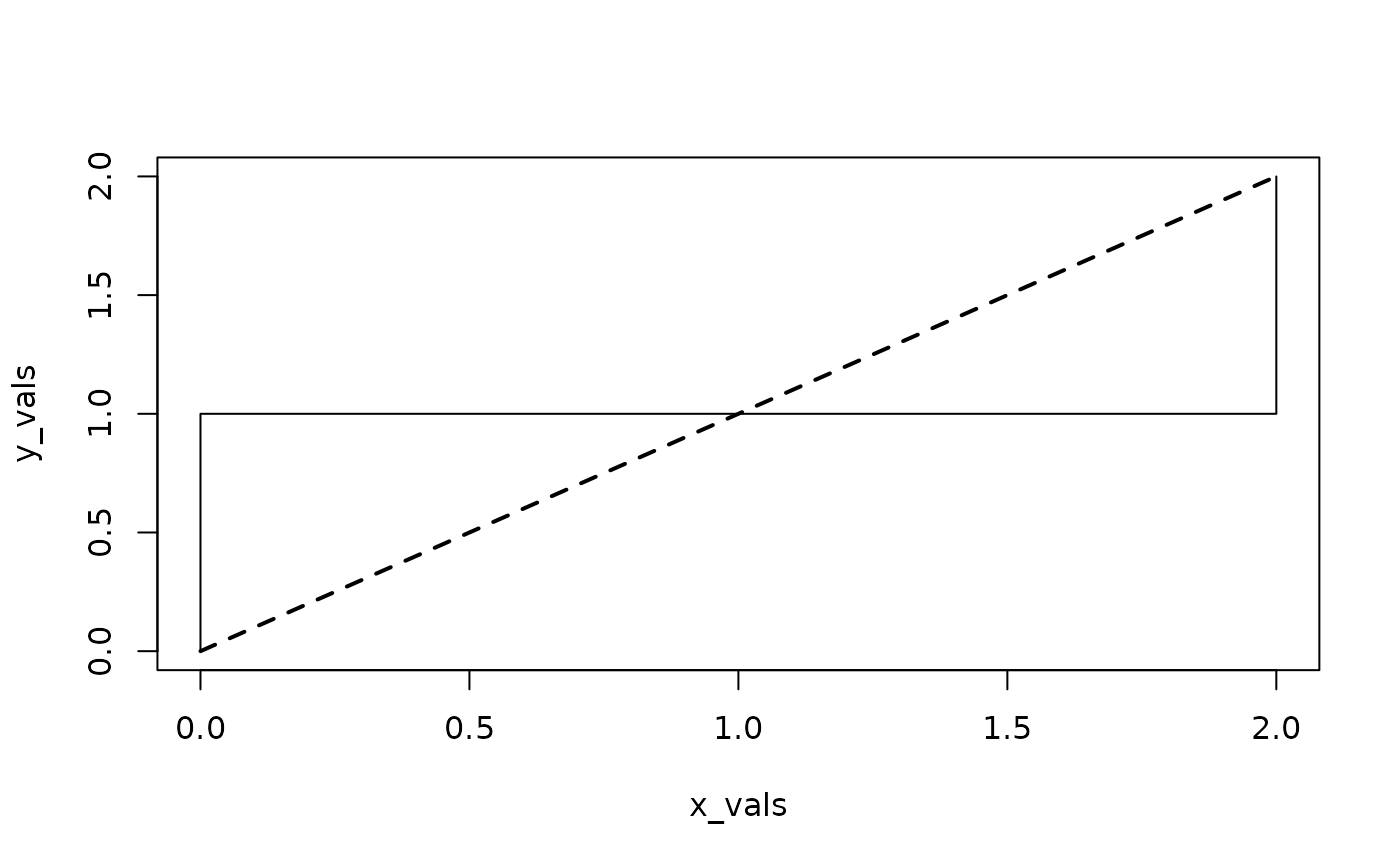
x_vals <- c(0, 0, 1, 2, 2)
y_vals <- c(0, 1, 1, 1, 2)
plot(x_vals, y_vals, type = "l")
lines(c(0, 2), c(0, 2), lty = "dashed", lwd = 2) # ideal
x_vals <- -x_vals
auc(x_vals, y_vals) # now it is counterclockwise again
#> [1] 2
x_vals <- c(0, 0, 1, 2, 2)
y_vals <- c(0, 1, 1, 1, 2)
plot(x_vals, y_vals, type = "l")
lines(c(0, 2), c(0, 2), lty = "dashed", lwd = 2) # ideal
 auc(x_vals, y_vals) # might create small rounding errors; this should be 0
#> [1] 3.330669e-16
all.equal(0, auc(x_vals, y_vals)) # indeed interpreted by R as basically 0
#> [1] TRUE
x_vals <- c(0, 1, 2, 1)
y_vals <- c(0, 1, 1, 0)
plot(x_vals, y_vals, type = "l")
lines(c(0, 1), c(0, 0), lty = "dashed", lwd = 2) # ideal
auc(x_vals, y_vals) # might create small rounding errors; this should be 0
#> [1] 3.330669e-16
all.equal(0, auc(x_vals, y_vals)) # indeed interpreted by R as basically 0
#> [1] TRUE
x_vals <- c(0, 1, 2, 1)
y_vals <- c(0, 1, 1, 0)
plot(x_vals, y_vals, type = "l")
lines(c(0, 1), c(0, 0), lty = "dashed", lwd = 2) # ideal
 auc(x_vals, y_vals)
#> [1] 2
auc(x_vals, y_vals, geometric = TRUE) # note the difference
#> [1] 1
auc(x_vals, y_vals)
#> [1] 2
auc(x_vals, y_vals, geometric = TRUE) # note the difference
#> [1] 1